As the world strives to transition to a low-carbon economy, the potential of hydrogen engine has gained prominence. These engines operate similarly to internal combustion engines but are specifically designed to burn hydrogen instead of fossil fuels.
By replacing traditional combustion with hydrogen combustion, the aim is to significantly reduce the emissions of greenhouse gases responsible for climate change.
In this article, we embark on an informative journey to uncover the inner workings of hydrogen engines, shedding light on their functionality and the potential benefits they offer. Join us as we explore the fascinating world of hydrogen-powered vehicles and the pivotal role they can play in shaping a greener future for automobiles.
With the escalating concerns about climate change and the environmental impact of traditional fossil fuel-powered vehicles, there is a pressing need to adopt cleaner and more sustainable forms of transportation.
Hydrogen, the most abundant element in the universe, has garnered considerable attention as a viable solution. It can be produced through various methods, including the electrolysis of water, and when used as a fuel, it emits zero harmful emissions. This makes hydrogen an exceptionally attractive alternative to conventional gasoline or diesel engines that contribute to air pollution and global warming.
Hydrogen As a Fuel in Hydrogen Engine
Produced through methods like the electrolysis of water, hydrogen possesses remarkable characteristics that make it an ideal energy source.
When used as a fuel, hydrogen combustion generates only water vapor as a byproduct, eliminating harmful emissions that contribute to air pollution and climate change.
This zero-emission attribute positions hydrogen as a cleaner alternative to conventional gasoline or diesel engines. Furthermore, hydrogen fuel cells, which convert hydrogen into electricity, offer high energy efficiency and can power various types of vehicles, presenting a versatile and sustainable solution for transportation needs.
With its abundance and environmental advantages, hydrogen fuel holds tremendous potential to revolutionize the way we power our vehicles and reduce our carbon footprint.
The Working Principle of a Hydrogen Engine
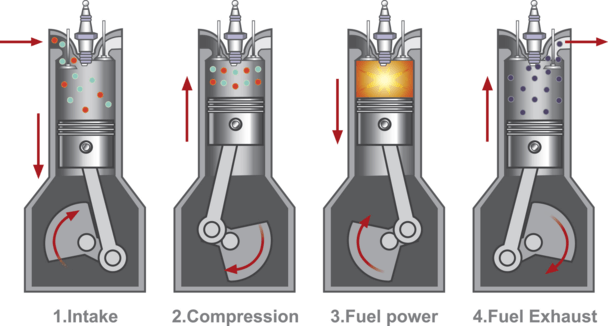
A hydrogen engine operates on a similar principle to an internal combustion engine but with modifications to accommodate the unique properties of hydrogen as a fuel.
Understanding the working principles of a hydrogen engine is essential to grasp its functionality and efficiency. Let’s explore the key components and processes involved in the operation of a hydrogen engine:
Intake System:
The intake system of a hydrogen engine controls the flow and mixture of air and hydrogen that enters the combustion chamber.
The intake manifold regulates the amount of hydrogen and air entering the engine, ensuring an optimal mixture for combustion. The precise control of this mixture is crucial for efficient combustion and power generation.
Combustion Chamber:
The combustion chamber is where the magic happens. In a hydrogen engine, hydrogen gas mixes with air to create a combustible mixture.
Unlike conventional gasoline engines that use spark plugs to ignite the mixture, hydrogen engines employ a fuel injector. The fuel injector sprays hydrogen into the combustion chamber in a fine mist, promoting even mixing with air.
Ignition:
Once the hydrogen-air mixture is compressed within the combustion chamber, the ignition process begins. A spark plug or, in some cases, a glow plug ignites the mixture, triggering combustion.
The heat generated by the ignition causes the hydrogen and air mixture to rapidly expand, resulting in a controlled explosion.
Combustion Process in Hydrogen Engine:
As the hydrogen and air mixture ignites, it undergoes a combustion process similar to that of a conventional engine. The energy released during combustion drives the engine’s pistons, which convert the pressure into rotational motion. This rotational motion is transferred to the crankshaft, enabling the generation of mechanical power.
Exhaust System:
After the combustion process, the byproduct of hydrogen combustion is water vapor. Unlike traditional engines that produce harmful emissions such as carbon dioxide and nitrogen oxides, a hydrogen engine’s only emission is water vapor, making it an environmentally friendly choice. The exhaust system of a hydrogen engine is designed to expel water vapor safely.
Cooling System:
Hydrogen combustion generates significant heat, and it is crucial to manage engine temperature effectively. Hydrogen engines employ cooling systems that circulate coolant, usually a mixture of water and ethylene glycol, to regulate the engine’s temperature.
The coolant absorbs the excess heat produced during combustion, preventing overheating and maintaining optimal operating conditions.
Hydrogen Storage:
To power a hydrogen engine, a reliable storage system is required to store and deliver hydrogen to the engine as needed. Hydrogen can be stored in gaseous or liquid form, depending on the specific design and requirements of the engine.
Common storage methods include high-pressure tanks for gaseous hydrogen and cryogenic tanks for liquid hydrogen. The storage system ensures a constant and reliable supply of hydrogen to the engine.
In Summary…
The hydrogen engine’s working principle involves a carefully controlled mixture of hydrogen and air in the combustion chamber.
The fuel injector delivers hydrogen into the chamber, and upon compression, ignition occurs through a spark plug.
The resulting combustion releases energy that drives the engine’s pistons, converting pressure into rotational motion.
The exhaust system expels the byproduct—water vapor—while the cooling system manages engine temperature.
With an efficient hydrogen storage system, hydrogen engines offer a sustainable and environmentally friendly solution for powering vehicles.
Understanding Deep Learning in Simple Words of a Layman
Benefits of Hydrogen Engines
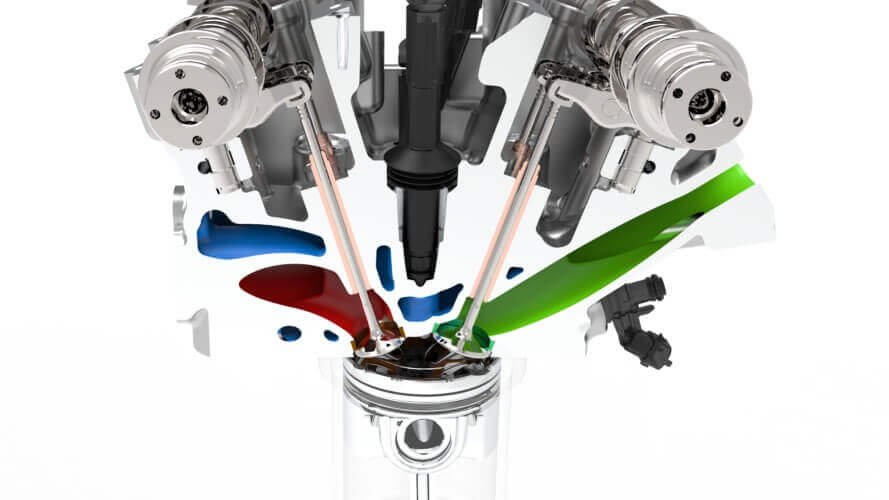

Hydrogen engines offer a range of significant advantages over conventional combustion engines, making them a promising solution for achieving sustainable transportation. Let’s explore the key benefits associated with hydrogen engines and how they contribute to a greener and more efficient future.
Zero Emissions:
One of the most compelling benefits of hydrogen engines is their ability to produce zero harmful emissions. Unlike internal combustion engines that burn fossil fuels and release carbon dioxide, nitrogen oxides, and other pollutants, hydrogen combustion solely produces water vapor as a byproduct.
This means that hydrogen engines have no detrimental impact on air quality and contribute to mitigating climate change by reducing greenhouse gas emissions. The absence of harmful emissions makes hydrogen engines a clean and environmentally friendly alternative.
High Efficiency:
Hydrogen engines are known for their high thermal efficiency, enabling them to convert a significant portion of the fuel’s energy into useful work. Internal combustion engines typically have lower thermal efficiencies due to energy losses in the form of heat and friction.
However, hydrogen engines can achieve efficiencies comparable to or even higher than other alternative powertrain technologies, such as electric vehicles. This higher efficiency translates into better mileage and energy savings, making hydrogen-powered vehicles an economically viable and sustainable option.
Versatile Applications:
Hydrogen engines can power a wide range of vehicles, including cars, buses, trucks, and even trains. This versatility makes hydrogen engines suitable for various transportation needs, from personal vehicles to public transportation and commercial fleets.
The ability to adapt hydrogen engines to different vehicle types and sizes enhances their potential to transform the entire transportation sector. Moreover, hydrogen engines can be integrated into existing vehicle platforms, simplifying the transition to hydrogen-based technologies.
Rapid Refueling:
One advantage of hydrogen engines over electric vehicles is their fast refueling capability. While electric vehicles require charging time, hydrogen vehicles can be refueled within minutes, similar to refueling a conventional gasoline or diesel vehicle.
This characteristic eliminates the concerns of range anxiety and allows for more convenient and flexible usage. Rapid refueling is particularly advantageous for commercial fleets or long-distance travel, where time efficiency is crucial.
Energy Storage and Grid Integration:
Hydrogen can play a vital role in energy storage and grid integration. Excess renewable energy generated from sources like solar or wind power can be used to produce hydrogen through electrolysis.
The hydrogen can then be stored and later utilized in hydrogen engines to generate electricity when needed. This process helps stabilize the electrical grid, manage fluctuations in renewable energy supply, and provide a clean and sustainable energy solution beyond transportation.
Reduced Noise Pollution:
Another benefit of hydrogen engines is their quieter operation compared to traditional combustion engines. Hydrogen engines produce lower noise levels, contributing to reduced noise pollution, especially in urban areas.
This characteristic enhances the driving experience and contributes to a more peaceful and pleasant environment for both drivers and pedestrians.
Understanding Deep Learning in Simple Words of a Layman
Challenges and Future Prospects
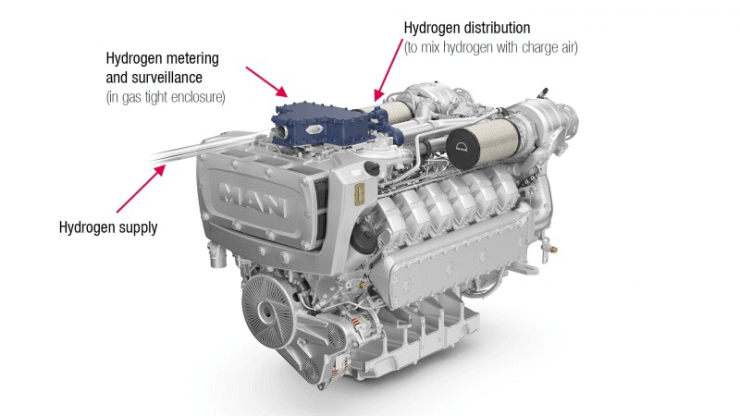
While hydrogen engines offer numerous benefits, there are still several challenges to overcome and prospects to consider to ensure their widespread adoption. Let’s explore some of the key challenges and potential solutions that will shape the future of hydrogen engines.
Hydrogen Production:
One significant challenge lies in the large-scale production of hydrogen. Currently, the majority of hydrogen is produced from fossil fuels, which undermines its potential as a clean energy source.
To fully realize the environmental benefits of hydrogen engines, it is crucial to transition to sustainable methods of hydrogen production. Renewable energy sources, such as solar and wind power, can be harnessed to power electrolysis, a process that splits water into hydrogen and oxygen.
By investing in renewable energy infrastructure and developing efficient electrolysis technologies, we can ensure a sustainable and carbon-neutral hydrogen supply.
Infrastructure Development:
Establishing a robust hydrogen fueling infrastructure is vital for the widespread adoption of hydrogen-powered vehicles. This includes building hydrogen refueling stations, storage facilities, and transportation networks to ensure a reliable supply of hydrogen fuel.
Currently, hydrogen infrastructure is limited compared to traditional gasoline stations or electric charging stations. Governments, industry stakeholders, and policymakers need to collaborate to incentivize the expansion of hydrogen infrastructure and overcome the chicken-and-egg dilemma of vehicle adoption and infrastructure development.
Cost Considerations:
The cost of hydrogen production, storage, and distribution is another significant challenge. Currently, hydrogen technologies are relatively expensive compared to conventional internal combustion engines or electric vehicles.
However, advancements in technology, economies of scale, and increased investment in hydrogen infrastructure are expected to drive down costs over time.
Research and development efforts are focused on improving the efficiency of hydrogen production methods and reducing the costs associated with hydrogen storage and transportation.
Safety Considerations:
While hydrogen itself is not inherently dangerous, safety concerns surrounding its storage and handling require attention. Hydrogen is highly flammable and has low ignition energy, making proper safety protocols and infrastructure critical.
Implementing stringent safety regulations and standards for hydrogen storage, transportation, and refueling systems is essential to ensure the safe integration of hydrogen engines into everyday transportation.
Public Perception and Awareness:
Public perception and awareness of hydrogen engines also play a crucial role in their acceptance and adoption. Educating the public about the benefits, safety, and potential of hydrogen engines is important to build confidence and overcome any misconceptions.
Demonstrating successful case studies and highlighting the environmental advantages can help garner support and encourage consumers to embrace hydrogen-powered vehicles.
Future Prospects:
Despite the challenges, the prospects for hydrogen engines are promising. Ongoing research and development efforts are focused on enhancing the efficiency and performance of hydrogen engine technologies.
Advancements in fuel cell technology, improved storage methods, and more efficient electrolysis processes are expected to make hydrogen engines more competitive and economically viable.
Moreover, hydrogen engines can complement other sustainable technologies such as electric vehicles and renewable energy sources. Integrated systems that combine hydrogen fuel cells and batteries can offer complementary advantages, such as extended range and rapid refueling.
This hybridization approach can further enhance the appeal and versatility of hydrogen-powered vehicles.
Additionally, governments and policymakers worldwide are recognizing the potential of hydrogen as a clean energy source. Various countries have initiated ambitious hydrogen strategies and investment plans to promote the development of hydrogen infrastructure and accelerate the adoption of hydrogen technologies. These initiatives, coupled with private sector investments, are likely to drive innovation and further propel the growth of the hydrogen economy.
Conclusion:
Hydrogen engines hold tremendous potential as a clean and efficient solution for sustainable transportation. With zero emissions, high efficiency, and versatile applications, they offer a promising pathway toward a greener future.
However, challenges such as hydrogen production, infrastructure development, cost considerations, safety, and public perception need to be addressed. Through continued research, technological advancements, and collaborative efforts among governments, industry stakeholders, and the public, these challenges can be overcome.
As we work towards sustainable hydrogen production, expand the infrastructure, reduce costs, ensure safety, and raise awareness, hydrogen engines have the opportunity to revolutionize the automotive industry and contribute to a cleaner and more sustainable transportation sector.
Embracing hydrogen as a fuel source will play a vital role in achieving our goals of mitigating climate change, reducing pollution, and fostering a greener and healthier planet for future generations.
FAQs about Hydrogen Engines and Cars:

Here are some Frequently Asked Questions about the Hydrogen Engine and Hydrogen Car:
What is a hydrogen engine?
A hydrogen engine is a type of internal combustion engine specifically designed to burn hydrogen as a fuel source. It operates similarly to conventional engines but uses hydrogen gas instead of gasoline or diesel to generate power.
How does a hydrogen engine work?
In a hydrogen engine, hydrogen gas mixes with air in the combustion chamber. The mixture is ignited, causing combustion and releasing energy.
The energy drives the engine’s pistons, which convert the pressure into rotational motion, powering the vehicle.
Are hydrogen engines more efficient than gasoline engines?
Yes, hydrogen engines can achieve higher thermal efficiencies compared to traditional gasoline engines. They convert a significant portion of the fuel’s energy into mechanical work, resulting in better mileage and energy savings.
Are hydrogen engines environmentally friendly?
Yes, hydrogen engines are considered environmentally friendly. They produce zero harmful emissions, with the only byproduct being water vapor.
This eliminates harmful greenhouse gas emissions, reduces air pollution, and helps combat climate change.
How do I refuel a hydrogen-powered car?
Refueling a hydrogen-powered car is similar to refueling a gasoline or diesel vehicle. Hydrogen refueling stations are equipped with nozzles that connect to the car’s hydrogen tank. The refueling process takes a few minutes, similar to conventional refueling.
Is hydrogen safe to use as a fuel?
Hydrogen is a highly flammable gas, but when handled properly and following safety protocols, it can be used safely as a fuel. Stringent safety measures are in place to ensure the safe storage, transportation, and refueling of hydrogen.
What are the challenges of hydrogen-powered vehicles?
Some challenges of hydrogen-powered vehicles include the production of hydrogen from sustainable sources, the development of a robust hydrogen refueling infrastructure, cost considerations, and public awareness and acceptance.
Can hydrogen-powered vehicles replace conventional gasoline vehicles?
Hydrogen-powered vehicles have the potential to be a significant part of the future transportation landscape.
However, a complete transition from conventional gasoline vehicles to hydrogen-powered vehicles would require addressing the challenges of infrastructure development, cost, and scaling up hydrogen production.
Are there any hydrogen-powered vehicles available for consumers?
Yes, hydrogen-powered vehicles are commercially available. Some automakers offer hydrogen fuel cell vehicles (FCVs) for consumers, such as the Toyota Mirai and Hyundai Nexo.
These vehicles utilize hydrogen fuel cells to generate electricity and power an electric motor.
What is the future of hydrogen-powered transportation?
The future of hydrogen-powered transportation looks promising. Ongoing research, investments, and policy support are driving advancements in hydrogen technologies.
As hydrogen production becomes more sustainable, infrastructure expands, costs decrease, and public awareness grows, hydrogen-powered transportation is expected to play a significant role in achieving sustainable mobility and reducing greenhouse gas emissions.
What is a hydrogen engine in space engineering?
A hydrogen engine in space engineering is a propulsion system that uses hydrogen as fuel to generate thrust for space vehicles. It’s known for its high efficiency, producing water vapor as a clean byproduct, making it suitable for space missions. However, challenges include handling cryogenic hydrogen and the complexity of infrastructure in space.



