Second Language Acquisition Theories set the path in front of us, how a person learns a new language other than its native language.
A child learns its native language by listening and comprehending the words and sentences from its surroundings but when it comes to a second language acquisition, it mostly depends on the learner itself and the degree of efforts that it puts for learning that language.
The learning process of the second language depends on a number of factors including age, motivation, and many other social factors.
The history of Second Language Acquisition Theories starts from the famous Philosopher Plato, who was a student of Socrates.
According to Plato, language is an innate character found in all living organisms because keeping in view the progress and age of Humans (just 30 to 35 years at that time) it was very difficult for a human being to understand the complex grammatical and semantic structures of a language.
This innate character was later called the Language Acquisition Device by Noam Chomsky(Famous Linguist).
Plato described no basic principles and practice in second language acquisition which was rather controversial and the debate went on to later philosophers.
Behaviorism
Behaviorism was originally discovered by BF Skinner which means that humans learn by imitation and experimentation and successively, develop their behavior on the basis of the outcome of the experiment if given reinforcement as well. In this way, habits are formed.
Skinner said these principles and practice in second language acquisition are the fundamentals of Behaviorism.
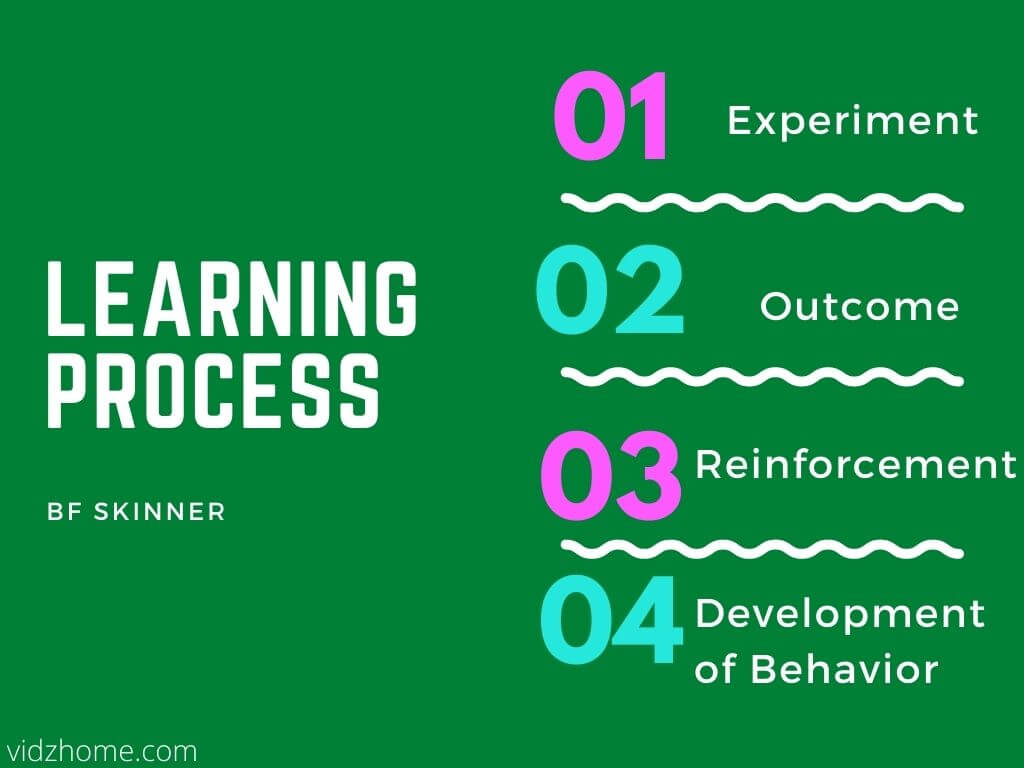
BF Skinner added to this theory of Behaviorism and experimented with this on different animals because he stated that this process of behaviorism is the same in humans and animals.
When a process is encouraged in an animal and becomes a part of its habits, it is called Positive Reinforcement.
On the other hand, when a process is discouraged in an animal and is removed from its habits, this is known as Negative Reinforcement.
Rat Experiment
BF Skinner performed the Rat Experiment to explore the principles and practices in second language acquisition.
He captured some rats in a cage and placed them in a cage where two buttons were given to them. If the rats pressed the first button they were given the food and alternatively if pressed the other button, they were given an electric shock.
As the rats started to understand the outcome of pressing the buttons and getting shocks they were just pressing the first button and never the other one.
In Language Learning
When a person imitates or mimics the words of a foreign language fluently, he is appreciated by his teacher or his friends and as a result, he keeps it in his memory.
But when the words are not mimicked properly, he is being scolded and as a result, he tries to correct himself and improves his second language day by day.
In this way, this second language acquisition theory is considered as the basics of all other theories.
Limitations
When children learn through this concept, they often overlap different concepts as a child may say, “I just eated a sandwich” you can see the problem in this phrase, he is overlapping the concept of a regular verb in an irregular verb.
Children are often unable to exactly copy the adults and in the try to copy they often say grammatical wrong lines.
The adults are most concerned about the truthfulness of the children and tend to make children more polite and true rather than grammatically correct.
However, this phenomenon is the most basic and applicable way of learning a language but is mostly concerned with learning the native language of the child.
Language Acquisition device (Innateness)

Noam Chomsky has objections to the principles and practice of Behaviorist theory in second language acquisition which prompted him on proposing his own theory of Innatism.
In Innatism, Noam Chomsky proposed that every child is born with an innate ability to learn a language that is programmed in his brain and often referred to as a Language acquisition device. However, he may require extensive knowledge of the grammar in that language.
Biological Basis of Language Acquisition
Modern linguistic studies have proved that language is a very complex phenomenon involving various syntactical rules which we apply thousands of times daily in our everyday speech.
So, the process of language acquisition is Biologically determined and these linguistic techniques are incorporated within the Neural System of a child at the time of its birth which assists us in understanding the principles and practices in second language acquisition.
This innate blessing of human beings is given the name of “Language Acquisition Device” which is a very special character of the human brain and signifies them from other living organisms who lack this special character.
Universal Grammar
These techniques are not conscious or based on a specific language but these are based on those common principles that every language shares and these language techniques are often referred to as Universal Grammar.
This Universal Grammar tells us how the words are put together to get the desired meaning although we gather the semantic meanings from our surroundings.
Chomsky argued, if humans had to learn this universal grammar then they could never be such fast and efficient learners of the language.
Limitations
This theory again had some limitations but this acted as a role model for the researches of many other Linguists.
According to Chomsky, children learn the words by hearing and arrange them according to a pattern that is common in every language like an English child observes that past forms of verbs contain ‘ed’ at the end but becomes confused when encounters irregular forms of verbs.
Monitor Model (By Stephen Krashen)

Krashen’s monitor model of second language acquisition consists of 5 hypothesis
Krashen has proposed the Monitor Model of Second Language Acquisition Theories which is based on these five points:
- Language Acquisition is unconscious (results from Informal or natural communication)
- Language Learning is conscious (Formal learning)
- Grammar structures are acquired in a natural order (i.e. predictable)
- Language acquisition occurs with comprehensible input (i.e. hearing or reading things that are just slightly above our current language level).
- A monitor is anything that corrects your language performance and pressures one to “communicate correctly and not just convey meaning” (such as a language teacher who corrects you when you make a grammatical mistake).
These 5 points are the basis of Krashen’s theory of second language acquisition and are closely interrelated to each other and are inspired by the Noam Chomsky theory of Language Acquisition.
Language Acquisition
This term of language acquisition refers to attaining First or Native Language which is entirely unconscious and results from informal and natural communication that is done with the child.
When adults communicate with or in front of the children they hear the words and sentence formation with those words and acquire the distinct patterns of that language.
This hypothesis of Krashen is more or less majorly based on principles and practice in second language acquisition proposed by Chomsky in his Universal Grammar model.
Language Learning
The phenomenon of language learning is more based on acquiring a second language which is mostly related to adults, not children.
According to Krashen, acquiring a second language is more of a formal process and takes place with full consciousness of the individual.
Natural and Predictable order of Learning
Everything in this universe works in a specific order, so is the learning. When a child starts learning a language(its first language), it learns it in a specific order.
So, if a person wants to learn a second language the principles and practice in that second language acquisition also take place in a natural and predictable order.
For Example
Like as a teacher, when I was teaching English to a student(adult) of mine, my first and foremost objective was to make him familiar with “English Alphabets and Sounds”
Then I started teaching him the way, these sounds connect to form words. In this way, he began to understand English.
The Comprehensible Input
It is the most important and significant aspect of Krashen’s theory of second language acquisition. He observed that a person only what, he is exposed to.
As a student of Language, I know that the only way to become fluent in a language is just by practicing that language with others.
For Example
You must have noticed that a person does not become fluent in a foreign language when he is just studying that language but when he goes to the country of that language’s native speaker, he automatically becomes fluent in it.
Role of Monitor in Second Language Learning
The monitor is someone, who takes care of your language by correcting any kind of error that the person encounters or guides him for every stage of learning.
If you ever had a tutor for learning any kind of skill then you may understand the importance of Monitor in learning that language because It is the same as having a tutor for learning something.
So, having a Monitor increases your learning exponentially because he corrects you and brings small changes in you for successful learning of a second language.
Krashen’s Monitor Model Example
Other Models of Second Language Acquisition Theories
Many other theories like Sociocultural, Constructivism, and Humanism are also acceptable nowadays but most of these theories are based on the above-mentioned basic theories.
Constructivism
This theory is based on Experience, as an individual gains experience of any language by practicing the Principles of that language, he gets to know about it and learns that language
Humanism
This theory is established on human behavior which is to satisfy the prior needs of humans for the effective learning of second stages as this phenomenon works in order:
- Basic needs like food and place to live
- Psychological needs like encouragement and esteem
- Self actualization
Sociocultural theory
According to this theory, when a person lives in a society, he interacts with the individuals of that society and talks to them and peers with them, and in turn, learns the language of that society.
This is not only the easiest way but also the most enjoyed and most efficient way of learning a language.
Conclusion
Acquiring or Learning a Second Language is quite different from learning the first or native language as the native language is learned by a child and the second language is learned by an adult having an entirely different approach as compared to the child.
These theories are the most basic among the principles and practices in second language acquisition. However, there are many other concepts known in the present date but these theories form the foundation of those second language acquisition theories.